Beginner's Guide to Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Supplements
If you’re reading this, chances are you’ve felt overwhelmed trying to unravel the complex connection between oxidative stress and chronic inflammation, and figuring out solutions that work.
You’re not alone!
First off, let's break down what oxidative stress is and why it's important to know about it. Think of oxidative stress as a troublemaker in your body. It happens when there's an imbalance between harmful substances and the good guys that fight them off. This imbalance can speed up aging and even lead to serious diseases like cancer. That's why doctors and health experts often talk about it – it's a big deal for your overall health.
Emerging research reveals the vital role your body's defense system plays against cell damage in disease prevention and longevity. As this system gets out of balance, millions have embarked on a relentless search to restore balance. Yet, trial and error with treatments often leads to more frustration - and questions about why benefits remain elusive while health challenges persist. These treatments help build up your body's natural defenses against harmful molecules known as free radicals, which can damage cells, leading to aging and various diseases.
The truth is, that finding what works for you requires deeper personalized insight. We all have individual differences in cell function, genetics, and lifestyle habits. And generic one-size-fits-all antioxidant recommendations from supplement companies and health influencers often miss the mark for many.
So is there a better way?
Welcome to the world of genetic testing.
By using advanced testing to measure the level of cell damage and inflammation happening inside your own body, you can get tailored nutrition recommendations matched to your unique biochemistry.
This personalized approach finally provides answers instead of guessing which antioxidants might help through trial and error. In simple terms, the tests show how much unwanted inflammation and cell harm is going on inside your body so we can recommend nutrients to counteract it.
Together, let’s cut through the hype and uncover smarter, simpler paths for you to use targeted antioxidant treatments. These can help fight the underlying factors causing your oxidative stress and regain the energy and wellness that is right for your body.
Let’s take a deeper look at oxidative stress and leap into its supplements — aka — the Antioxidants.
Oxidative Stress: What Happens When Body Balance Tips
As explained above, oxidative stress refers to an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body.
Free radicals are molecules produced during normal cell processes and are helpful in some processes like in immune function, but excessive amounts can be harmful. You can think of free radicals as the "troublemakers" that can damage cells and DNA if their population grows too large. Factors like pollution, smoking, poor diet, stress, and even intense exercise can increase free radical production.
Antioxidants are the "peacekeepers" that neutralize free radicals. They are found naturally in many fruits, vegetables, grains, herbs, and spices. Antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, polyphenols, carotenoids, etc., help prevent cell damage from free radicals and keep them at optimal levels.
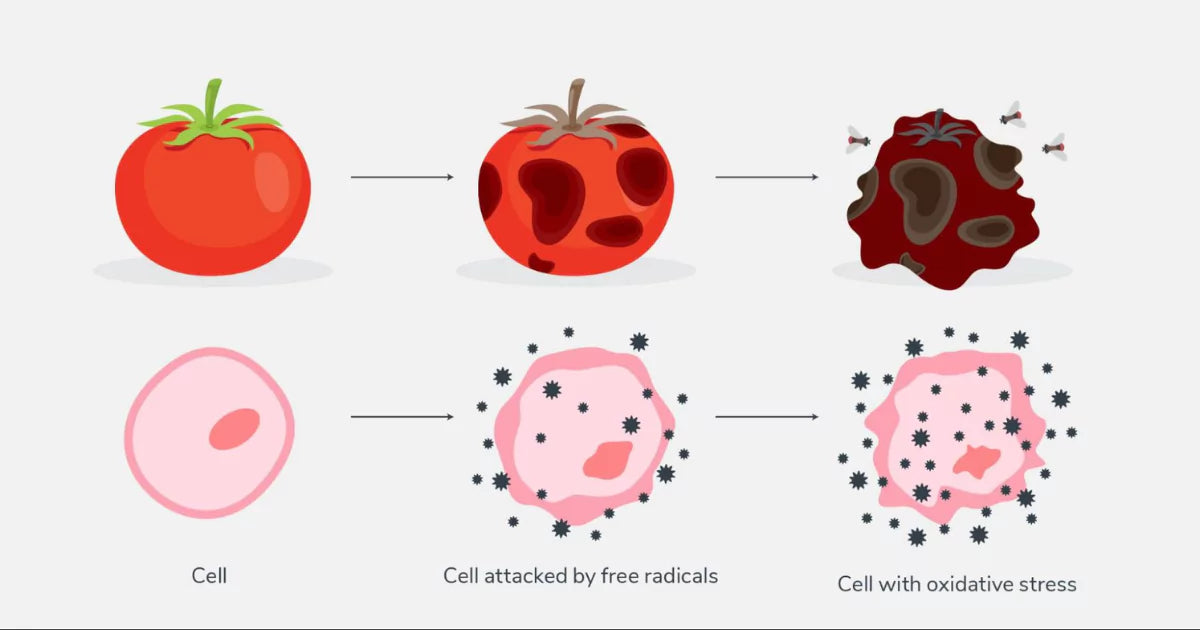
When there are not enough antioxidants to counter all the free radicals produced in your body and from environmental exposures, you experience oxidative stress. Too much oxidative stress has been connected to many diseases - including cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
The science behind oxidative stress is complex. But the basic concept is simple - ensure the "peacekeepers" are strong enough to handle the "troublemakers" through both diet and lifestyle measures for optimal well-being.
Which Substances Protect Against Oxidative Stress And The Resultant Cell Damage? The Antioxidants!
If oxidative stress is an imbalance between "troublemaker" free radicals and "peacekeeper" antioxidants, then antioxidants are what you want on your team. Let's understand why these little guys are so effective at combating oxidative damage such as DNA damage.
1. What Are Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are substances that can prevent or slow damage to cells caused by free radicals. These can be found in both synthetic and natural forms, with natural antioxidants being more commonly used due to their potential health benefits.
2. Natural Food Sources of Antioxidants
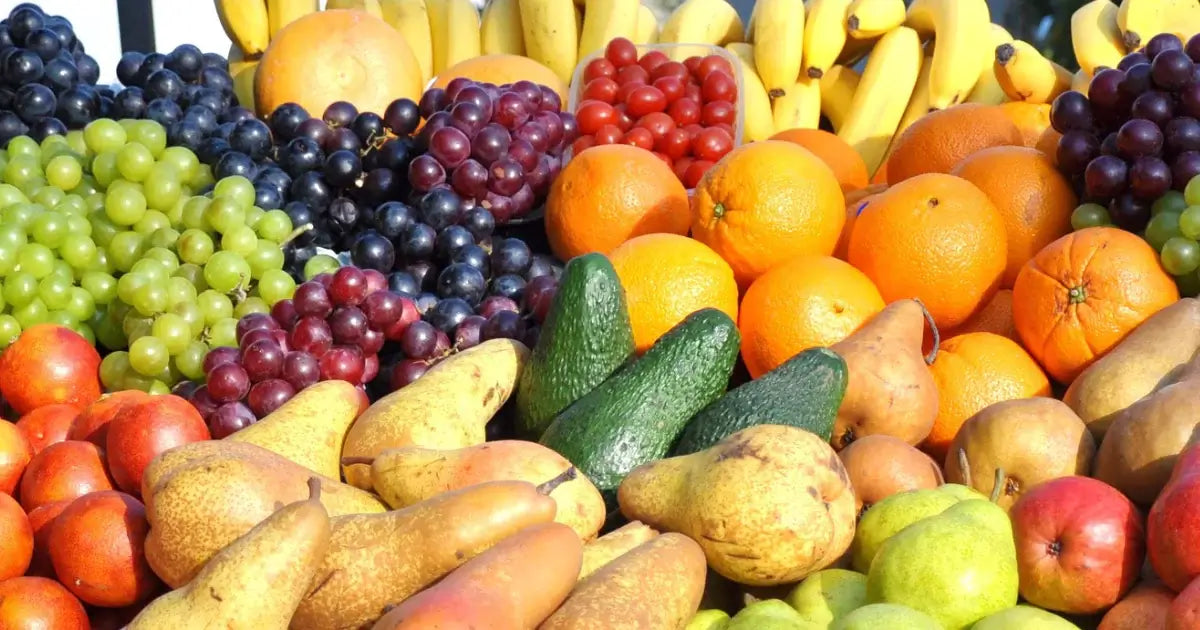

Natural food sources of antioxidants include:
- Fruits and vegetables: Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), dark leafy greens (spinach, kale), broccoli, artichokes, citrus fruits, cherries, and beans. These are rich in vitamins C and E, as well as other antioxidants like polyphenols and flavonoids.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds are high in antioxidants.
- Whole grains: Oats, brown rice, and quinoa are good sources of antioxidants.
- Lean meats, poultry, and fish: These foods contain antioxidants like copper and selenium.
- Herbs and spices: Turmeric, ginger, and cinnamon are rich in antioxidants.
3. How Antioxidants Help Combat Oxidative Stress
We already know that antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals, which can cause cellular damage and contribute to various health issues. Let’s now see how they work:
- Scavenging free radicals: Antioxidants can neutralize free radicals, preventing them from causing damage to cells and tissues.
- Promoting cellular repair: Some antioxidants, and glutathione, are involved in mechanisms that repair DNA and maintain the health of cells.
- Minerals such as manganese, selenium and iron are important nutrients that support the function of antioxidants that are produced naturally in our cells and act like “sparkplugs” called cofactors to ensure optimal function.
- Supporting overall health: A diet rich in antioxidants has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
How to Choose the Right Antioxidant Supplements
Selecting the right supplements is essential for optimizing health and well-being. Guidance from healthcare providers and considering potential benefits can help you make informed decisions about your supplementation. Here’s a quick guide how you can go about it:
1. Get a Genetics Test for Personalized Supplements
Everyone's body is different, and that includes how we all use antioxidants. That's where a DNA test can help. Genetic testing analyzes common variations that impact your body’s ability to use particular antioxidants.

Understanding your genetic predisposition allows you to choose the most impactful antioxidant supplements your body can properly utilize.
Personalized vitamins and supplements are designed to meet an individual's specific nutritional needs based on their biomarkers, diet, and lifestyle factors. This targeted supplementation is more likely to achieve oxidative balance than a generic one-size-fits-all approach.
|
Maximize Your Healthspan Trajectory Learn your personal risk factors, nutrient recommendations, and small lifestyle changes to balance your body's defenses against cell damage. |
2.Discuss Options With Your Healthcare Provider

A healthcare provider can help determine which supplements are necessary and safe based on an individual's medical history, current medications, and health goals. Additionally, a healthcare provider can help monitor the effectiveness of personalized supplementation and make adjustments as needed.
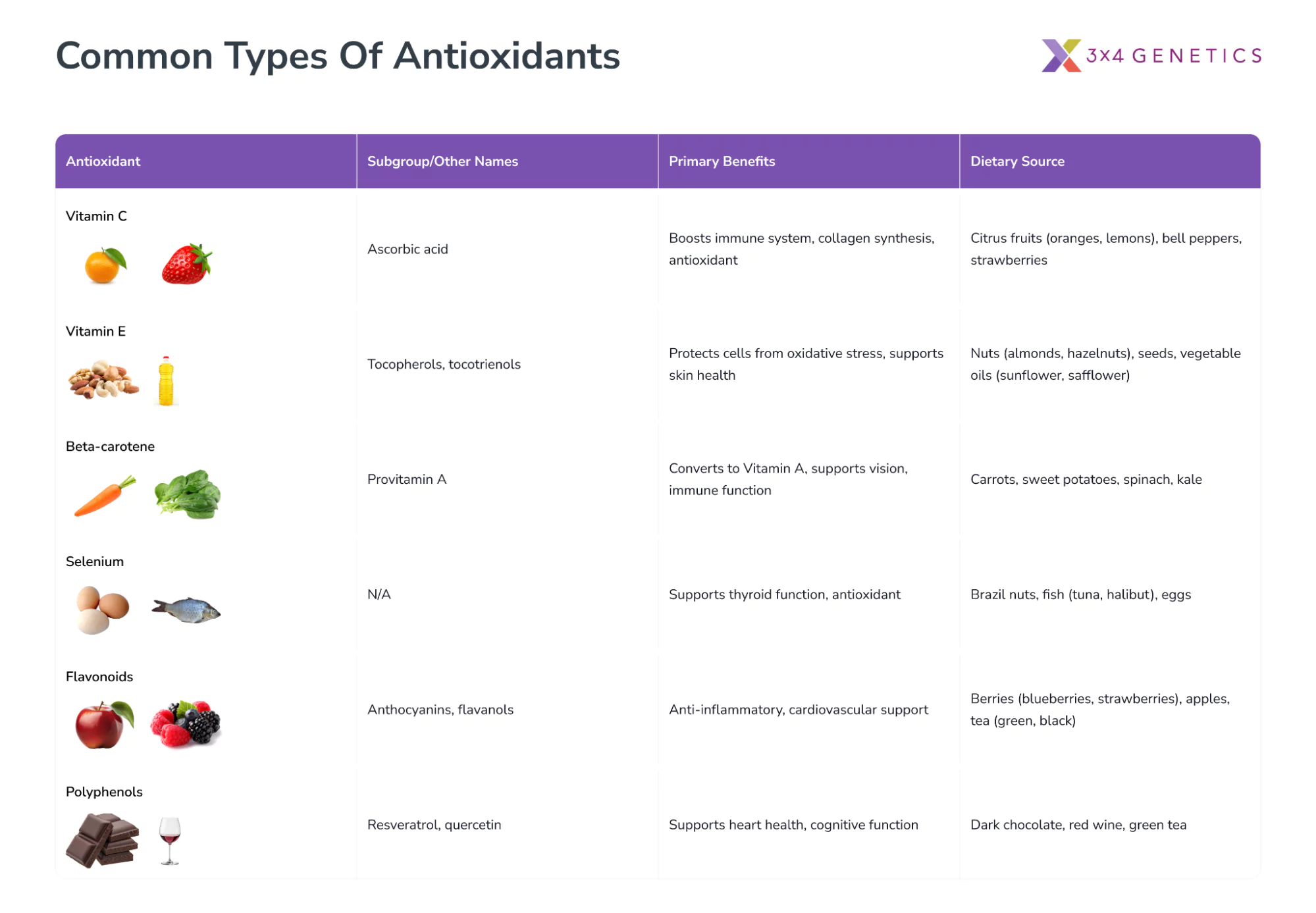
The Antioxidants You Should Know and Why They Matter
With so many different antioxidants available as supplements, it can get confusing trying to figure out which ones are best for you. Understanding the key antioxidant nutrients and what they do can empower you to make informed choices.
This knowledge is crucial because not all supplements are equally effective. The composition and doses influence the effectiveness. By learning the strengths of ingredients like vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, and glutathione, allows you to select products that match your personal goals - be that targeting aging, immunity, inflammation, or disease prevention.
|
Element |
Health Benefit |
|
|
Vitamin E |
Helps maintain healthy skin and eyes, and strengthen the body's natural defense against illness and infection (the immune system). |
Plant oils (such as rapeseed, sunflower, soya, corn, and olive oil), nuts and seeds, wheatgerm, and cereals and cereal products. |
|
Vitamin C |
Helps in supporting cell health, maintains skin, blood vessels, bones, cartilage, and aids wound healing. |
Citrus fruits (such as oranges and orange juice), peppers, strawberries, blackcurrants, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, potatoes, and other fruits and vegetables. |
|
Glutathione |
A powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative damage and supports immune function. |
Produced naturally in the body and obtained from certain foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and meat. |
|
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) |
NAC helps protect cells from oxidative damage and supports immune function. |
Commonly used as a dietary supplement and available as a prescription medication for certain medical conditions. |
|
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) |
Involved in the production of energy in cells, CoQ10 helps protect cells from oxidative damage and supports immune function. |
Found in small amounts in a wide variety of foods like spinach, broccoli, organ meats, soybeans, pistachio nuts etc. and available as a dietary supplement. |
|
Resveratrol |
A resveratrol is a type of polyphenol, which is a category of compounds naturally found in plant foods. It helps protect cells from oxidative damage and supports immune function. |
Most commonly associated with red wine and available as a dietary supplement. |
|
Curcumin |
A polyphenol found in turmeric, curcumin helps protect cells from oxidative damage and supports immune function. |
Commonly used as a spice in Indian cuisine and available as a dietary supplement. |
|
Green tea extract |
A source of polyphenols, green tea extract helps protect cells from oxidative damage and supports immune function. |
Made from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant and available as a dietary supplement. |
|
Selenium |
A trace element that helps the function of antioxidants naturally produced in cells, protect cells from oxidative damage and supports immune function. |
Found in various foods, including Brazil nuts, fish, and poultry. |
|
Zinc |
A trace element that helps protect cells from oxidative damage and supports immune function by ensuring optimal function of the body’s own antioxidant enzymes produced in the cells. |
Found in a wide variety of foods, including oysters, red meat, and poultry. |
Benefits of Personalized Antioxidant Supplements
Personalized supplementation of antioxidants can range from skin to strength.
For starters, antioxidants can delay muscle fatigue and give your workout performance a boost. They nourish skin from the inside out giving a smoother, firmer, more hydrated results.
Antioxidants can also benefit the functioning of our immune system!
Inflammation is a normal part of an immune response, but excessive or chronic inflammation can be detrimental over time. This type of persistent internal inflammation can weaken and dysregulate immune cells, compromising our defenses against pathogens. Now, antioxidants help counter this by reducing inflammatory signaling molecules and controlling the intensity of inflammation. In essence, they help ensure a balanced immune response - enough to combat viruses and bacteria when needed, but not so overzealous as to damage healthy tissue or impair immunity.
Antioxidants also play an important protective role in maintaining both cognitive vitality and heart health as we age. Regarding general heart health, oxidative stress creates inflammation in blood vessels and sets in motion the gradual development of atherosclerosis (build-up of plaque) in arteries, which can eventually lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Fortunately, consuming sufficient antioxidants from foods and supplements can help buffer our cells from these free radicals and oxidative damage.
Even respiratory conditions characterized by inflammatory flare ups like asthma may benefit from higher antioxidant intakes. Finally, an overall sense of wellness blooms when your body exists in an antioxidant-fueled balance rather than a state of distress from too much oxidative damage.
The point is, antioxidants touch nearly every aspect of health and function given how pervasive issues like inflammation and free radical reactions exist. Thrive inside and out with antioxidant support!
Last Thoughts on Boosting Your Defenses
Antioxidants deserve praise for the way they combat those chaotic free radicals, but we still need just the right amount of those troublemakers for good health too! After all, free radicals facilitate helpful roles like powering up our immune cells and signaling our genes to keep functioning smoothly.
Therefore, it is essential to consider individual genetic makeup when choosing the right supplements, as genetic variations can impact the body's response to specific supplements.
While antioxidants have tremendous potential, consulting your trusted healthcare practitioner lends key insight into personalizing a plan for your whole-person wellness vision. Who better to help assess your lifestyle factors and craft balanced guidance on any supplements or changes that serve you best?
Find out what delights YOUR individual biochemistry and plan accordingly!
FAQs related to Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Supplements
Q1: Are there lifestyle changes to reduce oxidative stress?
A: Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can help reduce oxidative stress.
Q2: What are antioxidant supplements, and do they work?
A: Antioxidant supplements are concentrated forms of antioxidants available in pill or capsule form. While they can be beneficial, it's essential to get most antioxidants from a diverse and balanced diet. Some studies suggest that high doses of certain antioxidant supplements may not be as effective or even harmful as they may dampen the body’s own natural ability to fight free radicals.
Q3: Can antioxidant supplements prevent diseases?
A: While antioxidants play a role in disease prevention, relying solely on supplements may not provide the same benefits as a well-rounded diet. It's crucial to consider overall lifestyle factors and a healthy diet for disease prevention.
Q4 Are there any risks associated with antioxidant supplements?
A: Yes, excessive intake of certain antioxidant supplements may have adverse effects. For example, high doses of vitamin E, C or beta-carotene may increase the risk of certain diseases. It's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
Q5: What is the best supplement for oxidative stress?
A: Identifying the "best" supplement for oxidative stress depends on individual health needs. Commonly recommended supplements include Vitamin C, Vitamin E, glutathione, and coenzyme Q10. However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice as they are not always effective in high doses or when taken regularly.
Q6: What antioxidants reduce oxidative stress?
A: Several antioxidants are known to effectively reduce oxidative stress. These include Vitamin C, Vitamin E, beta-carotene, selenium, glutathione, and flavonoids found in fruits and vegetables. Consuming a variety of antioxidant-rich foods as part of a balanced diet is the most effective way to combat oxidative stress.


